Satellite-based monitoring for national screening of agricultural fields parameters to support the Danish authorities . . .

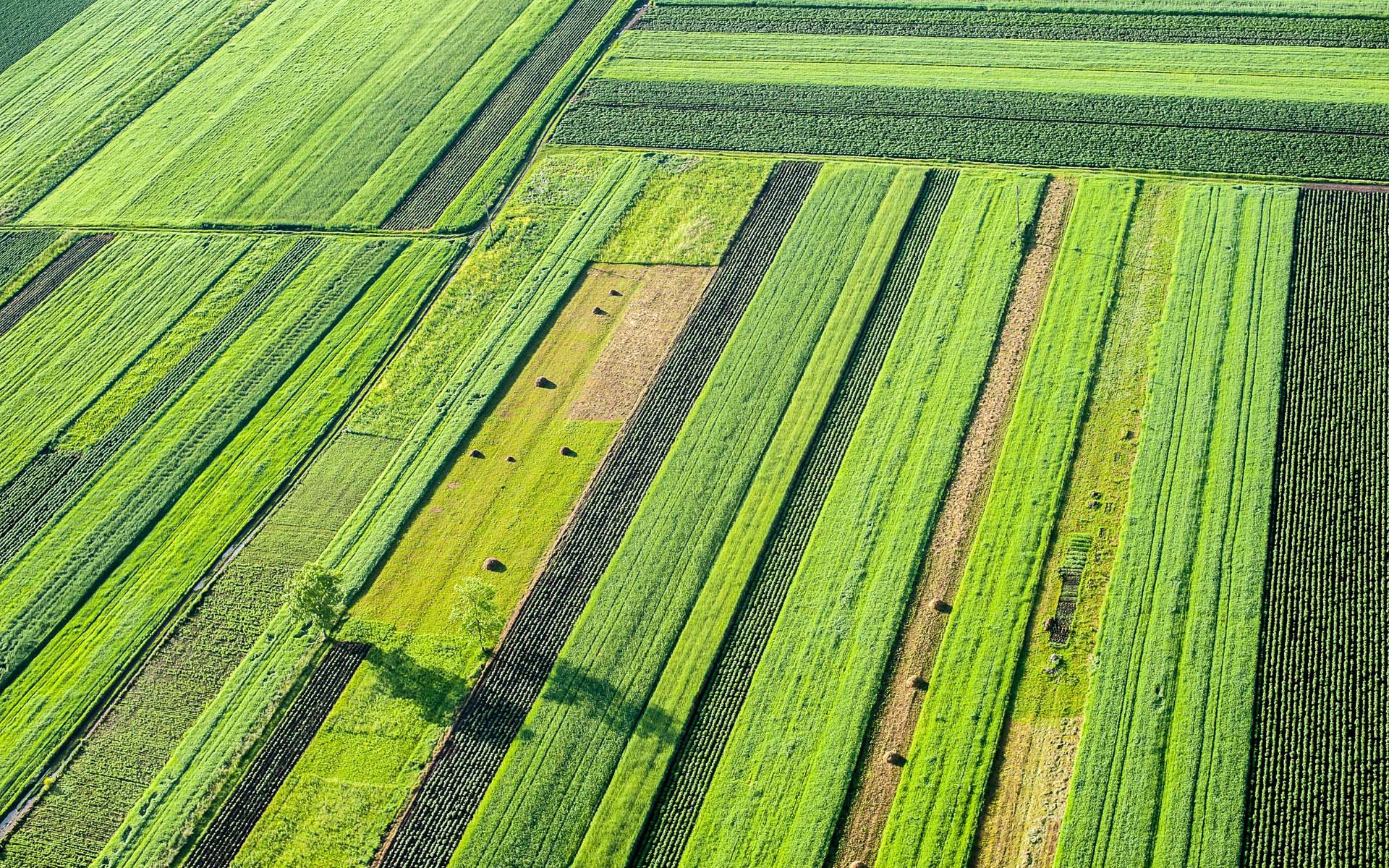
Monitoring agricultural fields using satellite images
Satellite-based monitoring for national screening of agricultural parameters to support the Danish authorities for agricultural control and CAP monitoring
How we helped:
Machine Learning and Data Fusion for crop-type monitoring. By building a likelihood model based on timing of the main crop harvest, the timing of parcel tillage after the main harvest and the field greenness in the September period to monitor the presence of catch crops.
Project highlights:
Building a national operating system for deriving agricultural parameters based on time series of both SAR and optical satellite data
Development of a user friendly web viewer for visualizing data and results allowing the user to search for specific field parcels and associated attribute information
Analysing time series based on advanced Machine Learning methods and data fusion for crop monitoring and likelihood model for monitoring of harvest and catch crops
In more detail..
The Danish Agricultural Agency is today performing control visits to field parcels across the entire country, to check if farmers report correctly on their crop types and farm management practices related to the CAP.
This line of work constitutes a significant work load and involves many field visits. The Danish Agricultural Agency needed a solution to check if farmers were reporting correctly in accordance with CAP requirements while at the same time reducing the amount of time spent on control visits.
All satellite data and results were presented on a web viewer developed to meet the client’s needs for assessing the satellite-derived information to be used in their CAP monitoring.
In short, we provided the Danish Agricultural Agency with:
- Crop classification of more than 18 different crop types
- Catch crop monitoring
- Detection of timing of harvest and grass tillage
- Detection of timing of ploughing
- Maize field monitoring
Danish Agricultural Agency:
The staff of the Danish Agricultural Agency, a total of approximately 1,200, strives countrywide to create the optimal conditions for sustainable growth and green transformation in the fields of Agriculture and Plants and horticulture.
They administer and provide grants for agricultural production, environmental and ecosystem improvements, development programmes, grants for minor projects, and administer subsidies for certain types of export.
EOatDHI part of the DHI GROUP
gras@dhigroup.com
+45 4516 9100
Agern Alle 5,
2970 Hørsholm,
Denmark
CVR: 36466871