DK4HAPS
Exploring uptake and innovation potential for services enabled by High Altitude Pseudo Satellites (HAPS) platforms in Denmark.
Why is it important?
As a future technology, HAPS platforms will open a new market for remote sensing and surveillance by offering disruptive and complementary applications to services enabled by satellites, terrestrial infrastructures and Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS), at relatively low cost. This project will explore uptake potential among stakeholders in Denmark and identify potential use case applications in a Danish context.
Project highlights:
Analysing and documenting opportunities for HAPS platforms to contribute to, and strengthen, the capacity of the Danish authorities to carry out surveillance and monitoring tasks, primarily in the field of defense and security.
Documenting existing HAPS technology gaps, to uncover industry needs and requirements, in order to leverage opportunities for Danish tech companies to contribute relevant technology that can support the development of HAPS platforms.
Provision of tailormade workshops focusing on HAPS application potential and opportunities, to connect industry leaders and relevant stakeholders in the uptake community and explore relevant use case scenarios in Denmark.
In more detail..
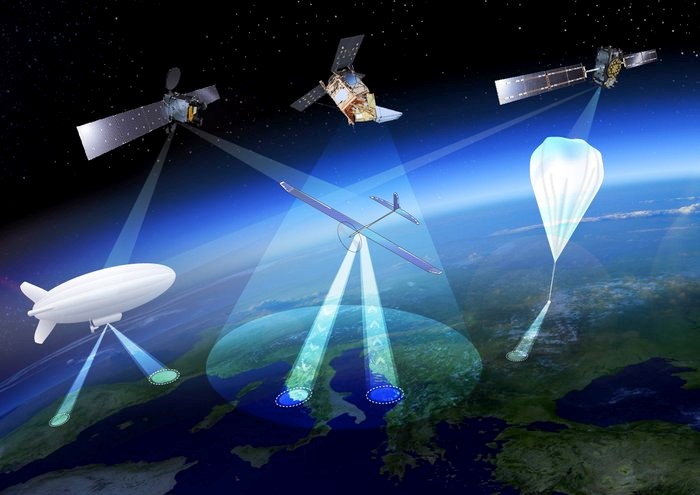
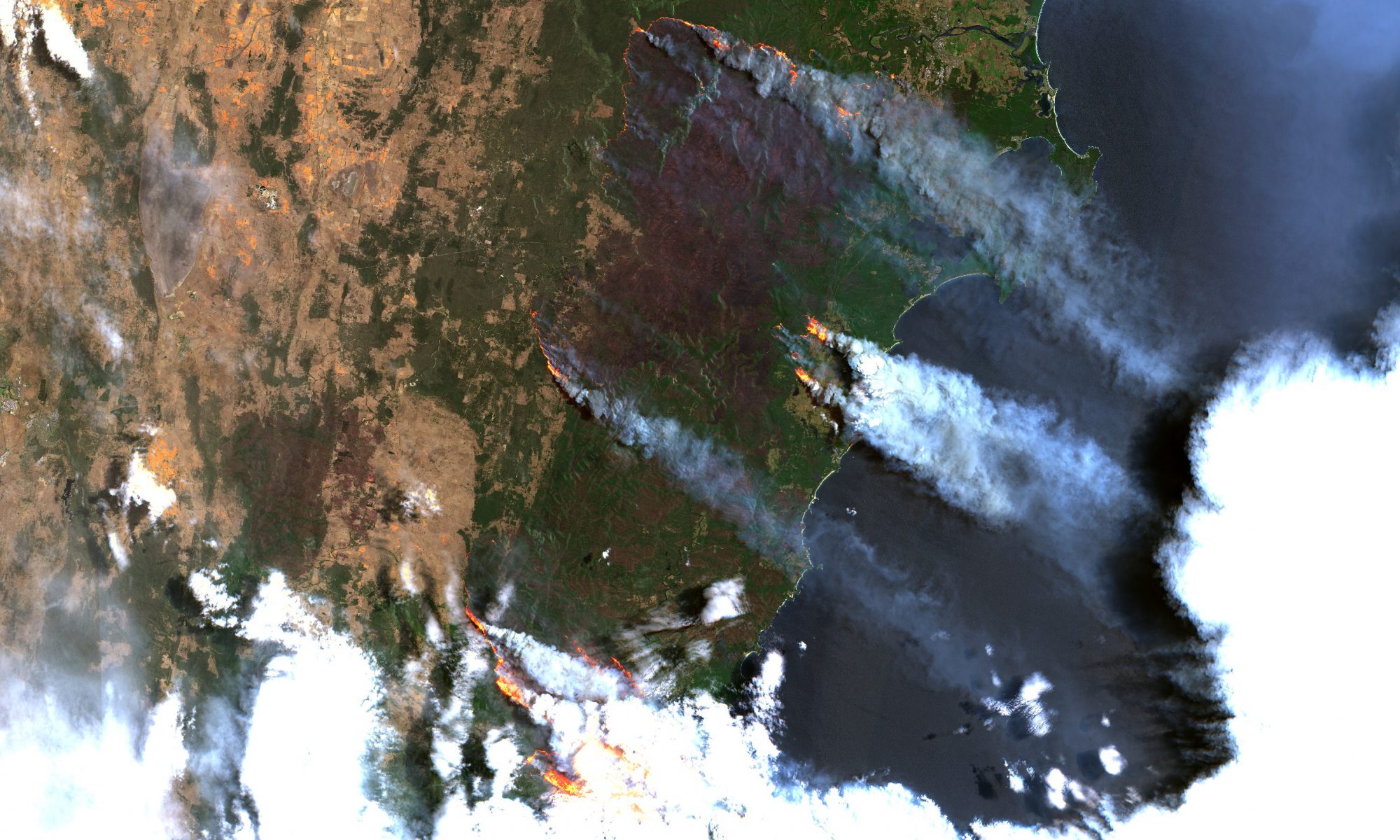
High Altitude Pseudo Satellites (HAPS) are geostationary or quasi-stationary stratospheric platforms that provide a link between the capabilities of satellites, UAVs and aircrafts. Positioned in the lower stratosphere, at a height of just over 20 km, they are close enough to the earth to provide high spatial resolution video and image data and at a distance far enough to uncover large land and ocean areas, continuously and in near real time.
They are ideally positioned to complement and expand the capabilities of satellites in earth observation, telecommunications and navigation and provide time-critical and permanent monitoring and communication solutions at relatively low cost.
Therefore, in the near future, HAPS platforms are expected to open up a new market for remote monitoring, enabling a time-critical and satellite-like monitoring that can support and contribute to several state and private applications and surveillance missions in defense and security, including patrol in Arctic, ship and air traffic monitoring, border patrol, etc.
This project aims to define the specific need for HAPS-based monitoring solutions in Denmark and at the same time identify opportunities for Danish technology companies to contribute relevant technology that can support the development of HAPS solutions, including the development of miniaturized sensors and communication systems.
Center for Defence, Space & Security:
The Center for Defence, Space & Security (CenSec) is the prime Danish cluster for small and medium-sized enterprises specializing in high tech industries like defence, homeland security, space, aerospace, railway and maritime.
CenSec was founded in 2004 and established in 2007 as an industrial cluster. In 2018, CenSec was approved by the Danish Ministry of Higher Education and Science to also become a national Innovation Network for Security (Inno-Sec)
EOatDHI part of the DHI GROUP
gras@dhigroup.com
+45 4516 9100
Agern Alle 5,
2970 Hørsholm,
Denmark
CVR: 36466871