EO Clinic: Snow and Ice Mapping in Kazakhstan
Delivering satellite derived information on snow and ice dynamics to the Kazakh Space Agency.
Why is it important?
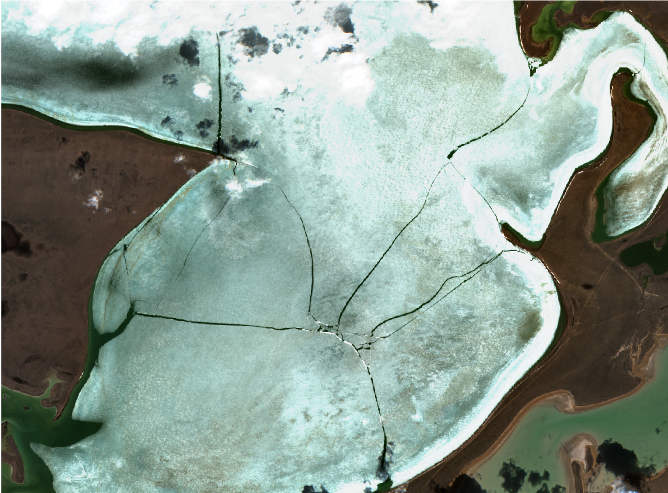
The snowpack and its spatial and temporal variability play an important role in the hydrological cycle and water resource management of Kazakhstan, since most rivers and streams are fed by snow melt, which is the main water source for the vegetation growing season. Snow stores a significant mass of water and knowledge about the extent and amount of water provides important input for hydrodynamic models and the management of natural hazards, such as flood events. River ice controls the winter flow regime of rivers and compromises the operation of hydrometric stations, governs the water intake and discharge activities of municipalities and businesses. Particularly during spring, break-up ice can create jams and floods that endanger infrastructure such as bridges. EO based information could feed into a near real time monitoring system to support informed decision making.
Project highlights:
Possibility for near real-time monitoring systems for ice jam detection.
Improved forecasting of snowmelt runoff to inform flood warning tools.
Input for hydrodynamic models for informed decision making.
In more detail..
The Committee on Water Resources of the Ministry of Ecology, Geology and Natural Resources and the Committee for Emergency Situations of the Ministry of Internal Affairs has appointed the Kazakh space agency (Kazakhstan Gharysh Sapary - KGS) to provide solutions to mitigate flood-related hazards and risks. The application of Earth Observation (EO) data is a very efficient and cost-effective way to support flood protection programs. EO’s strength lies in its large-area and high-temporal monitoring capabilities of the Earth’s surface - information of direct relevance to better understand the water dynamics, flood occurrence and finally inform hydrodynamic models to improve flood simulations.
Despite its importance, snow cover, one of the Essential Climate Variables, is often underrepresented in such models. Snow stores a significant mass of water and, with its high dynamic, has a strong effect on regional and global energy and water cycles. Information of ice dynamics can inform tools to monitor risk-prone areas in near real time such as ice jams along rivers that potentially endanger infrastructure or provoke flooding.
In this project, DHI GRAS provided the following five products to KGS:
1. Snow Cover Extent
The snowpack and its spatial and temporal variability play an important role in the hydrological cycle and water resource management of Kazakhstan, since most rivers and streams are fed by snow melt, which is the main water source for the vegetation growing season.
2. Snow Water Equivalent
SWE represents the amount of water that is contained in a snowpack, i.e., the weight of the meltwater per square meter that would result if the snowpack was melted entirely. Information about SWE is needed in applications such as flood forecasting and irrigation planning.
3. Wet Snow Maps
Maps of wet snow can be used as indicator for onset of snow melt and inform hydrodynamic models.
4. Ice break-up
Ice break-up is an important hydrologic event with detriments, such as infrastructure damage and lost economic activity. Ice break-up is defined as a process with specific dates identifying key events between the onset of melt and the complete disappearance of ice.
5. Ice jam detection
River ice controls the winter flow regime of rivers and compromises the operation of hydrometric stations, governs the water intake and discharge activities of municipalities and businesses. Particularly during spring break-up, ice can create jams and floods that endanger infrastructure such as bridges with large economic losses.
EO Clinic
This project was carried out in the framework of the EO Clinic, in partnership between ESA (European Space Agency), the Asian Development Bank (ADB).
The activity is carried out within the scope of the recent ADB Knowledge and support Technical Assistance (KSTA) focusing on streamlining the use of high-level technologies in Kazakhstan and aligned with the operational priorities for ADB country partnerships and the National Sustainable Development Strategy of Kazakhstan.
EOatDHI part of the DHI GROUP
gras@dhigroup.com
+45 4516 9100
Agern Alle 5,
2970 Hørsholm,
Denmark
CVR: 36466871